Temporal Bone Blunt Trauma, pediatric, CT
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CA0307-Temporal Bone Blunt Trauma, pediatric, CT
 View Images
View Images
CA0307-Temporal Bone Blunt Trauma, pediatric, CT
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Prior Study
Findings
Facial and Scalp Soft Tissues and Airway
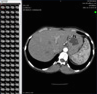
There is localized edema in the scalp soft tissues over the left mastoid and periauricular region.
Intracranial and Calvarium
There is no calvarial fracture and no subperiosteal, epidural or subdural hematoma and/or pneumocephalus along the boney walls of the anterior, middle or posterior cranial fossa or elsewhere.
There lack of clear differentiation of gray and white matter in the left temporal lobe and punctate areas of increased density in the cortex of the left frontal region and just above the orbit on the right; the latter may be volume averaging of the orbital roof. The study cannot exclude cerebral contusion and minimal cortical bleeding.
Right Temporal Bone
The right temporal bone is normal.
Left Temporal Bone
The external auditory canal is filled with abnormal soft tissue and/or blood thickening and fractured. The fracture, importantly, extends into the petrotympanic fissure. This petrotympanic region fracture narrows the protympanum junction with the bony Eustachian tube.
The fracture It also may extend into the mesial aspect of the condylar fossa.
There is middle ear or mastoid mucosal disease/fluid and the mastoid septae are disrupted. A mastoid fracture extends obliquely through the air cells from the lateral wall of the mastoid to its roof about 1 cm lateral to the arcuate eminence.
This fracture pattern raises the possibility of a CSF leak is based on the extensive fluid/blood/mucosal thickening in the mastoid as well as the displaced mastoid roof fracture.
The sigmoid plate of the mastoid is not fractured. The ossicles, in particular the incus long process, the incudostapedial joint and stapes are not fractured or dislocated.
The facial canal and the inner ear are not involved and there is
no air within the membranous labyrinth.
There is no fracture crossing the transverse sinus and no extra axial bleeding involving the posterior fossa.
Midface - Maxillary region
There is no evidence of a midface injury.
Fronto- naso - ethmoidal complex
There is no injury of the fronto-nasal- ethmoid complex.
Zygomatico-orbital region and globes
The zygomatic arch, frontozygomatic suture or infraorbital rim or lateral wall of the orbit are not fractured. There is no fracture of the greater or lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, optic strut and canal, or basisphenoid, in the region of the orbital apex.
Central Skull Base
There is fracture of basisphenoid. This is manifest as a buckle type of injury that is best identified on series 5 images 62 – 67 on the right side with a more subtle nondisplaced fracture seen on series 5 image 62 on the left.
Mandible and Temporomandibular Joints
There is nondisplaced fracture of the left condylar fossa.
Dentition
There are no dental fractures and/or missing or displaced teeth.
Cervical spine
The visualized portions of the cervical spine are normal for the patient’s age.
