Peritonsillar Abscess, CT
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CA0128-Peritonsillar Abscess, CT
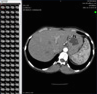 View Images
View Images
CA0128-Peritonsillar Abscess, CT
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Findings
Nasopharynx Including Retropharyngeal Lymph Nodes
There is hypertrophy and inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil with some accumulation of inflammatory luminal secretions in the left lateral pharyngeal recess but no evidence of nasopharyngeal abscess. There is minimal reactive retropharyngeal lymphadenopathy.
Oropharynx
There is hypertrophy and inflammation of the palatine tonsils with no obvious drainable fluid collection in the tonsils although there are some foci of early suppuration likely. In addition, on the left side there is a peritonsillar abscess. There is associated edema within the adjacent parapharyngeal space but the abscess is confined by the constrictors of the pharyngeal wall.
Cervical Lymph Nodes
There is reactive cervical lymphadenopathy predominantly, as expected at level 2. Some of these lymph nodes show early cellulitic change but there is no definite no suppurative lymphadenopathy.
Vascular Findings
There is no evidence of thrombus, thrombophlebitis or other occlusive or inflammatory process of the jugular vein or smaller venous tributaries.
The remainder of the visceral compartment of the head neck region and deep neck structures as well as the spine are within normal limits for the patient’s age.
Upper Lung Zones and Mediastinum
The upper lung zones and mediastinum visualized are normal.
Other Findings
Other significant abnormal findings are not present.
